Full glaze products are the mainstream trend category of the domestic ceramic tile industry in the past ten years, and glaze pinhole defects are the most common in the production of full glaze products, and it is also one of the production defects that are difficult to completely avoid, which directly affects the glaze quality effect of the product and the excellent rate of the finished product. There are many factors that cause pinhole defects, including blanks, glazes, production process parameters and firing systems, etc., and glazes include full glaze and face glaze, this paper mainly studies the influence of face glaze formula composition on pinhole defects, discusses the relationship between flux ratio and total amount in the formula with wide firing range and wide range of application, and the relationship between high temperature material ratio and total volume, and discusses the solution to rapid and effective control and reduce glaze pinhole defects.
The test was completed in a well-known ceramic enterprise in Qingyuan, the length of the kiln was 325m, the firing cycle was 48min, the ring temperature was 1166-1168 °C, the face glaze was applied by scraping glaze, and the glaze was applied by the glaze method for full glaze, and the number of pinhole defects in the area of 400mm ×800mm was calculated. The composition of the green body, the full glaze and the raw materials used for the glaze used in the test are shown in Table 1.
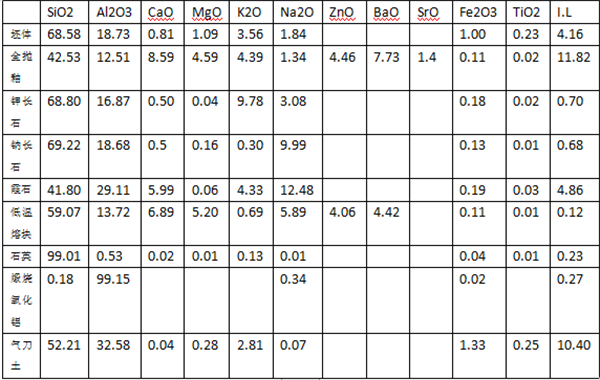
2.1 Test of the influence of flux ratio and burnt soil/burnt aluminum ratio on pinholes
Original: albite 12, potassium feldspar 31, quartz 20, gas knife earth 10, burnt aluminum 22, low temperature frit 3, nepheline 7, zirconium silicate 9.
A two-factor 3-level test is designed on the basis of the original square, including factor A – flux ratio, factor B – burnt soil/burnt aluminum ratio (quartz, gas knife earth, low temperature frit amount remains unchanged).
A: potassium feldspar, albite for nepheline in a ratio of 3:1:3, level A1 (albite / potassium feldspar / nepheline = 11/28/10), A2 (albite / potassium feldspar / nepheline = 10/25/13), A3 (albite / potassium feldspar / nepheline = 9/22/16)
B: Burnt aluminum for burnt soil according to the ratio of 3:5, B1 (burnt aluminum/burnt soil = 19/6), B2 (burnt aluminum/burnt soil = 16/11), B3 (burnt aluminum/burnt soil = 13/16)
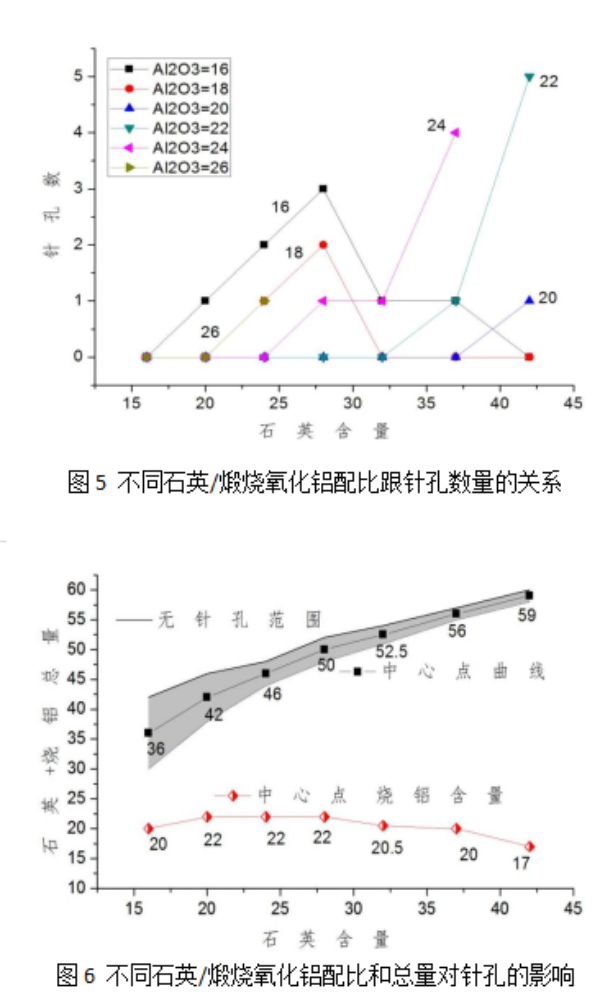
There are many factors that cause pinhole defects, and it is particularly critical to debug and optimize the formula composition and wide firing range of non-pinhole-free full glazed glaze. With the increase of the proportion of nepheline in the glaze formula, the proportion of potassium feldspar and albite decreased, and the pinholes showed a decreasing trend. With the increase of the proportion of burnt soil, the proportion of calcined alumina decreases, and the pinholes show an increasing trend, and vice versa. The more soil and quartz content in the formula, the narrower the pinhole-free area, the smaller the scope of application of the formula, the more the content of nepheline and calcined alumina, the wider the scope of the formula without pinholes, and the wider the scope of application of the formula.
(1) Pinholes are divided into two types: low-temperature pinholes and high-temperature pinholes, and the general characteristics of low-temperature pinholes are: the number of pinholes is large, the size is small, accompanied by a large number of prickly defects, and the single bottom glaze is basically not absorbent or very slight; The general characteristics of high-temperature pinholes are: the number of pinholes is small, the size is large, the prickly heat is less, accompanied by crater defects, and the single-bottom glaze is heavier in ink absorption.
(2) For pinhole defects in production, it is first necessary to determine whether it is a low-temperature pinhole or a high-temperature pinhole, according to the actual situation, calcined alumina is preferred to solve the low-temperature pinhole, and nepheline is preferred to treat the high-temperature pinhole.
(3) Quartz as a high-temperature material in the bottom glaze formula to improve the surface glaze maturity temperature and high temperature viscosity is far less obvious than calcined alumina, and the more quartz content, the smaller the area without pinholes, the narrower the scope of application of the formula.
Contents from FOSHAN CERAMIC MEGACINE
Post time: Nov-21-2022